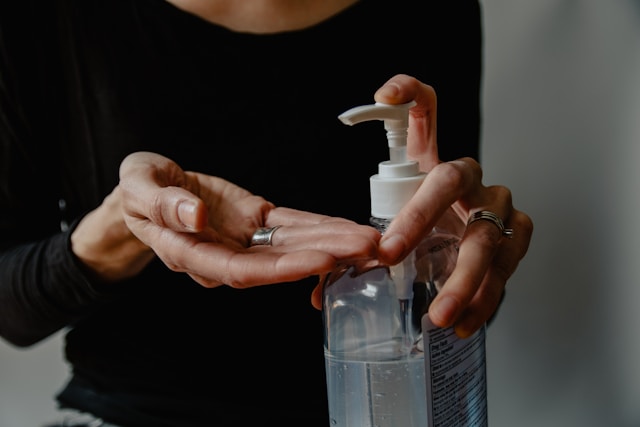
Hand hygiene is a fundamental aspect of personal hygiene that plays a critical role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. From common colds to more serious illnesses like COVID-19, practicing good hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to protect yourself and others from getting sick. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of proper hand hygiene in disease prevention, discuss the key principles of hand hygiene, and provide practical tips for maintaining clean hands in various settings.
Understanding the Role of Hands in Disease Transmission
Hands are one of the primary pathways for transmitting infectious agents from person to person. Throughout the day, our hands come into contact with surfaces that may be contaminated with bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. When we touch our face, mouth, nose, or eyes with dirty hands, we can introduce these pathogens into our bodies, increasing the risk of infection.
Key Principles of Hand Hygiene
Proper hand hygiene involves both washing hands with soap and water and using alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap and water are not available. The key principles of hand hygiene include:
- Frequent Handwashing: Wash your hands regularly, especially before eating, after using the bathroom, after coughing or sneezing, and after touching potentially contaminated surfaces;
- Thorough Washing Technique: Use soap and water to lather your hands thoroughly, covering all surfaces, including the backs of your hands, between your fingers, and under your nails. Rub your hands together for at least 20 seconds before rinsing thoroughly with water;
- Use of Hand Sanitizer: When soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol content. Apply enough sanitizer to cover all surfaces of your hands and rub them together until dry;
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Minimize touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, with unwashed hands to prevent the transfer of pathogens;
- Practice Respiratory Hygiene: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent the spread of respiratory droplets that can contaminate your hands and surfaces.
Benefits of Proper Hand Hygiene
Maintaining proper hand hygiene offers several important benefits:
- Reduces Disease Transmission: Regular handwashing and sanitizing significantly reduce the transmission of infectious agents, helping to prevent the spread of illnesses within communities;
- Protects Against Infections: Clean hands protect individuals from contracting common illnesses like colds, flu, and gastrointestinal infections, as well as more serious diseases like COVID-19;
- Promotes Public Health: By practicing good hand hygiene, individuals contribute to the overall health and well-being of society, especially during disease outbreaks and pandemics;
- Prevents Antibiotic Resistance: Proper hand hygiene helps reduce the need for antibiotics by preventing infections, which in turn helps combat the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Clean Hands
In addition to following the key principles of hand hygiene, here are some practical tips for maintaining clean hands in various settings:
- Carry Hand Sanitizer: Keep a travel-sized bottle of hand sanitizer with you for use when soap and water are not available, such as when traveling or running errands;
- Encourage Handwashing: Educate children and family members about the importance of handwashing and make it a regular part of daily routines, especially before meals and after using the bathroom;
- Use Gloves When Necessary: Wear gloves when handling potentially contaminated items or when providing care to sick individuals, but remember to remove and dispose of them properly and wash your hands afterward;
- Practice Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings: Healthcare workers should follow strict hand hygiene protocols, including handwashing before and after patient contact, to prevent healthcare-associated infections.
Conclusion
Proper hand hygiene is a simple yet powerful tool for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. By washing hands regularly with soap and water and using hand sanitizer when needed, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of getting sick and protect the health of others. As we continue to navigate through times of increased disease transmission, maintaining good hand hygiene practices remains essential for promoting public health and well-being.